Basic Swagger Info
Let's look at the various parts of the Petstore application Swagger UI to see how they are defined.
The top part of the page shows general information about the REST interface:
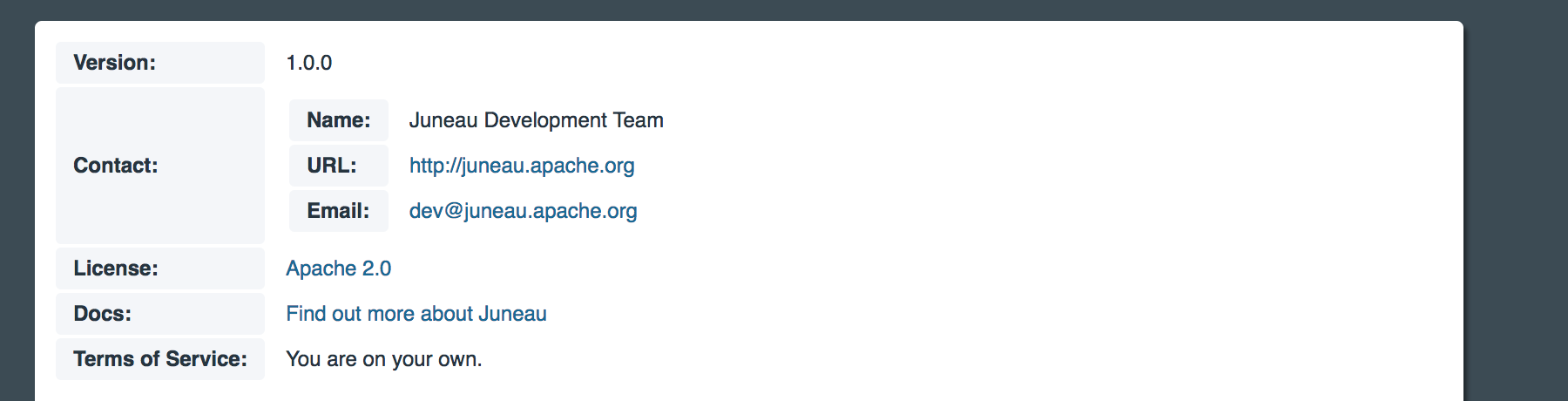
The information is pulled from the @Rest(swagger) annotation.
org.apache.juneau.examples.rest.petstore.PetStoreResource
@Rest(
path="/petstore",
title="Petstore application",
...
swagger=@Swagger("$F{PetStoreResource.json}"),
...
)
public class PetStoreResource extends BasicRestServlet {...}
In this particular case, the Swagger is pulled in from a localized Swagger JSON file located in the org.apache.juneau.examples.rest.petstore package using the $F variable.
PetStoreResource.json
{
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"version": "1.0.0",
"title": "Swagger Petstore",
"termsOfService": "You are on your own.",
"contact": {
"name": "Juneau Development Team",
"email": "dev@juneau.apache.org",
"url": "http://juneau.apache.org"
},
"license": {
"name": "Apache 2.0",
"url": "http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html"
}
},
"externalDocs": {
"description": "Find out more about Juneau",
"url": "http://juneau.apache.org"
},
...
}
Note that the $F variable allows for request-locale-sensitive name matching so that you can provide localized Swagger information. The $F variable simply expands to a string to fill the @Swagger(value) annotation. You could equivalently embed JSON directly into your annotation like so:
@Rest(
path="/petstore",
title="Petstore application",
...
swagger=@Swagger(
// Raw JSON5.
// Values are concatenated.
"{",
"swagger: '2.0',",
"version: '1.0.0',",
...
"}"
),
...
)
public class PetStoreResource extends BasicRestServlet {...}
However, a more typical (and less error-prone) scenario is to define all of your Swagger as annotations:
@Rest(
path="/petstore",
title="Petstore application",
...
swagger=@Swagger(
version="1.0.0",
title="Swagger Petstore",
termsOfService="You are on your own.",
contact=@Contact(
name="Juneau Development Team",
email="dev@juneau.apache.org",
url="http://juneau.apache.org"
),
license=@License(
name="Apache 2.0",
url="http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html"
),
externalDocs=@ExternalDocs(
description="Find out more about Juneau",
url="http://juneau.apache.org"
)
),
...
)
public class PetStoreResource extends BasicRestServlet {...}
All annotations support SVL Variables, so you could for example pull localized strings from resource bundles using $L variables.
@Rest(
path="/petstore",
title="Petstore application",
messages="nls/MyMessages",
...
swagger=@Swagger(
version="1.0.0",
title="$L{myTitle}",
termsOfService="$L{myTermsOfService}",
contact=@Contact(
name="$L{myTeam}",
email="dev@juneau.apache.org",
url="http://juneau.apache.org"
),
license=@License(
name="Apache 2.0",
url="http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html"
),
externalDocs=@ExternalDocs(
description="$L{myExternalDocsDescription}",
url="http://juneau.apache.org"
)
),
...
)
public class PetStoreResource extends BasicRestServlet {...}
A third option is to define your Swagger information in your @Rest(messages) resource bundle using predefined Swagger keywords:
PetStoreResource.version = 1.0.0
PetStoreResource.title = Swagger Petstore
PetStoreResource.termsOfService = You are on your own.
PetStoreResource.contact = {name:'Juneau Development Team', email:'dev@juneau.apache.org',...}
PetStoreResource.license = {name:'Apache 2.0',...}
PetStoreResource.externalDocs = {description:'Find out more about Juneau',...}
Information defined in multiple locations are merged into a single set of data. When the same information is provided in multiple locations, the following order-of-precedence is used:
- Java annotations
- Resource bundle
- Swagger JSON file
Share feedback or follow-up questions for this page directly through GitHub.