REST Server
@Rest-Annotated Resources
A REST resource is simply a Java class annotated with Rest. The most common case is a class that extends BasicRestServlet, which itself is simply an extension of HttpServlet which allows it to be deployed as a servlet.
// Sample REST resource that prints out a simple "Hello world!" message.
@Rest(
path="/helloWorld",
title="Hello World",
description="An example of the simplest-possible resource"
)
@HtmlDoc(
navlinks={
"up: request:/..",
"options: servlet:/?method=OPTIONS"
},
aside={
"This page shows a resource that simply response with a 'Hello world!' message",
"The POJO serialized is a simple String.",
}
)
@BeanConfig(sortProperties="true")
public class HelloWorldResource extends BasicRestServlet {
@RestGet(path="/*", summary="Responds with \"Hello world!\"")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello world!";
}
}
This is what it looks like in a browser.
http://localhost:10000/helloWorld
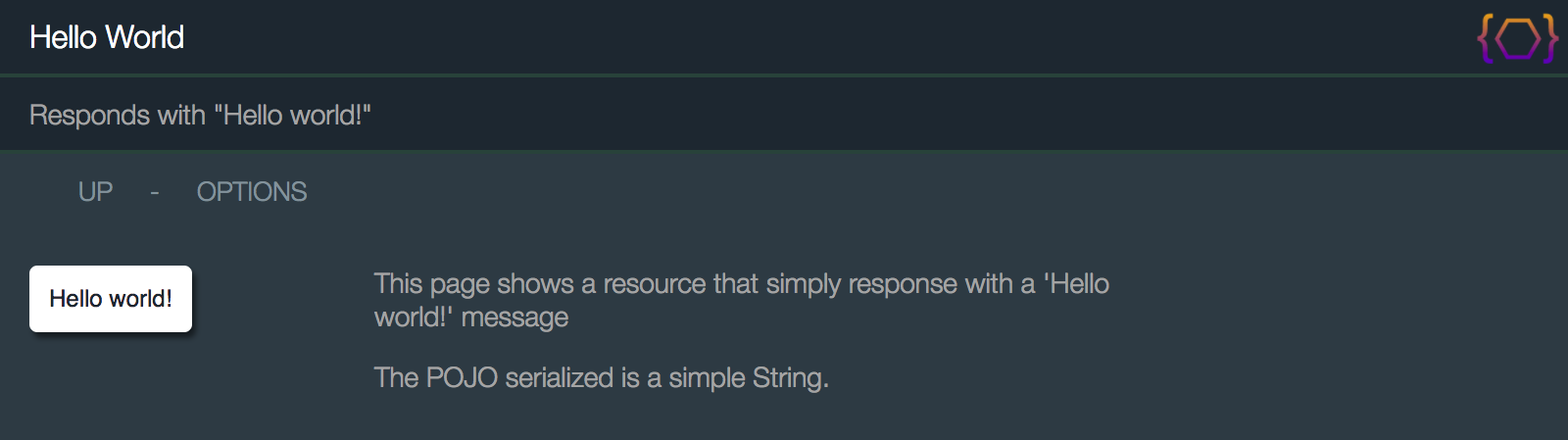
- Parsers for request bodies are selected based on the request
Content-Typeheader. - Serializers for response bodies are selected based on the request
Acceptheader. - In this case, it's the HtmlDocSerializer serializer based on the browser's default
Acceptheader that's asking for HTML.
REST resource classes and methods can be annotated with configuration annotations for the serializers and parsers (such
as @HtmlConfig and @BeanConfig shown above).
- Annotations such as the title, summary, and descriptions shown above are used for auto-generated Swagger UI pages (described later).
REST Children
Child Resources are REST servlets or objects that are linked to parent resources through the @Rest(children) annotation.
/** Parent Resource */
@Rest(
path="/parent",
children={
MyChildResource.class
}
)
public MyParentResource extends BasicRestServlet {...}
/** Child Resource */
@Rest(
path="/child" // Path relative to parent resource.
)
// Note that we don't need to extend from RestServlet.
public MyChildResource implements BasicRestObject {
...
}
The path of the child resource gets appended to the path of the parent resource. So in the example above, the child resource is accessed through the URL /parent/child.
The advantage of using child resources is that they do not need to be declared in the JEE web.xml file.
Initialization of and access to the child resources occurs through the parent resource.
Children can be nested arbitrary deep to create complex REST interfaces with a single top-level REST servlet.
Predefined Configuration Interfaces
The servlets in the previous section implemented the BasicUniversalConfig which simply defines a preconfigured set of annotations that get inherited by the child classes:
/**
* Predefined configuration for a REST resource that supports all languages
* and provides common default configuration values.
*/
@Rest(
// Default serializers for all Java methods in the class.
serializers={
HtmlDocSerializer.class,
HtmlStrippedDocSerializer.class,
HtmlSchemaDocSerializer.class,
JsonSerializer.class,
Json5Serializer.class,
JsonSchemaSerializer.class,
XmlDocSerializer.class,
UonSerializer.class,
UrlEncodingSerializer.class,
OpenApiSerializer.class,
MsgPackSerializer.class,
SoapXmlSerializer.class,
PlainTextSerializer.class,
CsvSerializer.class
},
// Default parsers for all Java methods in the class.
parsers={
JsonParser.class,
Json5Parser.class,
XmlParser.class,
HtmlParser.class,
UonParser.class,
UrlEncodingParser.class,
OpenApiParser.class,
MsgPackParser.class,
PlainTextParser.class,
CsvParser.class
}
)
public interface BasicUniversalConfig extends DefaultConfig, DefaultHtmlConfig {}
/**
* Predefined REST configuration that defines common default values for all configurations.
*/
@Rest(
// Configuration file.
config="$S{j.configFile,$E{J_CONFIG_FILE,SYSTEM_DEFAULT}}",
// Standard fields.
path="",
roleGuard="",
rolesDeclared="",
// Configuration beans.
converters={},
encoders={IdentityEncoder.class},
guards={},
parsers={},
partParser=OpenApiParser.class,
partSerializer=OpenApiSerializer.class,
responseProcessors={
ReaderProcessor.class,
InputStreamProcessor.class,
ThrowableProcessor.class,
HttpResponseProcessor.class,
HttpResourceProcessor.class,
HttpEntityProcessor.class,
ResponseBeanProcessor.class,
PlainTextPojoProcessor.class,
SerializedPojoProcessor.class
},
restOpArgs={
AttributeArg.class,
ContentArg.class,
FormDataArg.class,
HasFormDataArg.class,
HasQueryArg.class,
HeaderArg.class,
HttpServletRequestArgs.class,
HttpServletResponseArgs.class,
HttpSessionArgs.class,
InputStreamParserArg.class,
MethodArg.class,
ParserArg.class,
PathArg.class,
QueryArg.class,
ReaderParserArg.class,
RequestBeanArg.class,
ResponseBeanArg.class,
ResponseHeaderArg.class,
ResponseCodeArg.class,
RestContextArgs.class,
RestSessionArgs.class,
RestOpContextArgs.class,
RestOpSessionArgs.class,
RestRequestArgs.class,
RestResponseArgs.class,
DefaultArg.class
},
serializers={},
// Configurable settings.
allowedHeaderParams="$S{j.allowedHeaderParams,$E{J_ALLOWED_HEADER_PARAMS,Accept,Content-Type}}",
allowedMethodHeaders="$S{j.allowedMethodHeaders,$E{J_ALLOWED_METHOD_HEADERS,}}",
allowedMethodParams="$S{j.allowedMethodParams,$E{J_ALLOWED_METHOD_PARAMS,HEAD,OPTIONS}}",
clientVersionHeader="$S{j.clientVersionHeader,$E{J_CLIENT_VERSION_HEADER,Client-Version}}",
debug="$S{j.debug,$E{J_DEBUG,}}",
debugOn="$S{j.debugOn,$E{J_DEBUG_ON,}}",
defaultAccept="$S{j.defaultAccept,$E{J_DEFAULT_ACCEPT,}}",
defaultCharset="$S{j.defaultCharset,$E{J_DEFAULT_CHARSET,UTF-8}}",
defaultContentType="$S{j.defaultContentType,$E{J_DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE,}}",
defaultRequestAttributes="$S{j.defaultRequestAttributes,$E{J_DEFAULT_REQUEST_ATTRIBUTES,}}",
defaultRequestHeaders="$S{j.defaultRequestHeaders,$E{J_DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS,}}",
defaultResponseHeaders="$S{j.defaultResponseHeaders,$E{J_DEFAULT_RESPONSE_HEADERS,}}",
disableContentParam="$S{j.disableContentParam,$E{J_DISABLE_CONTENT_PARAM,false}}",
maxInput="$S{j.maxInput,$E{J_MAX_INPUT,1000000}}",
messages="$S{j.messages,$E{J_MESSAGES,}}",
renderResponseStackTraces="$S{j.renderResponseStackTraces,$E{J_RENDER_RESPONSE_STACK_TRACES,false}}",
uriAuthority="$S{j.uriAuthority,$E{J_URI_AUTHORITY,}}",
uriContext="$S{j.uriContext,$E{J_URI_CONTEXT,}}",
uriRelativity="$S{j.uriRelativity,$E{J_URI_RELATIVITY,}}",
uriResolution="$S{j.uriResolution,$E{J_URI_RESOLUTION,}}",
// Metadata settings.
consumes={},
description="",
produces={},
siteName="$S{j.siteName,$E{J_SITE_NAME,}}",
swagger=@Swagger,
title="$S{j.title,$E{J_TITLE,}}",
// Injectable/overridable beans.
beanStore=BeanStore.Void.class, // Defaults to BeanStore.
callLogger=CallLogger.Void.class, // Defaults to BasicCallLogger.
debugEnablement=DebugEnablement.Void.class, // Defaults to BasicDefaultEnablement.
fileFinder=FileFinder.Void.class, // Defaults to BasicFileFinder.
staticFiles=StaticFiles.Void.class, // Defaults to BasicStaticFiles.
swaggerProvider=SwaggerProvider.Void.class, // Defaults to BasicSwaggerProvider.
// Overridable context classes.
contextClass=RestContext.class,
restChildrenClass=RestChildren.class,
restOpContextClass=RestOpContext.class,
restOperationsClass=RestOperations.class
)
@BeanConfig(
// When parsing generated beans, ignore unknown properties
// that may only exist as getters and not setters.
ignoreUnknownBeanProperties="true",
ignoreUnknownEnumValues="true"
)
@SerializerConfig(
// Enable automatic resolution of URI objects to root-relative values.
uriResolution="ROOT_RELATIVE"
)
public interface DefaultConfig {}
/**
* Predefined REST configuration that defines common default values the HTML Doc serializer.
*/
@HtmlDocConfig(
// Default page header contents.
header={
"$RS{title}", // Use @Rest(title)
"$RS{operationSummary,description}", // Use either @RestOp(summary) or @Rest(description)
"$C{REST/header}" // Extra header HTML defined in external config file.
},
// Basic page navigation links.
navlinks={
"up: request:/.."
},
// Default stylesheet to use for the page.
// Can be overridden from external config file.
// Default is DevOps look-and-feel (aka Depression look-and-feel).
stylesheet="$C{REST/theme,servlet:/htdocs/themes/devops.css}",
// Default contents to add to the section of the HTML page.
// Use it to add a favicon link to the page.
head="$C{REST/head}",
// No default page footer contents.
// Can be overridden from external config file.
footer="$C{REST/footer}",
// By default, table cell contents should not wrap.
nowrap="true"
)
public interface DefaultHtmlConfig {}
The org.apache.juneau.rest.config package contains other basic configurations for use. Annotations are aggregated from child-to-parent order allowing for these basic configurations to be extended and modified, or you can create your own annotations from scratch.
REST Group Pages
The BasicRestServletGroup class provides a default "router" page for child resources when a parent resource is nothing more than a grouping of child resources. The RootResources class in the Samples project is an example of a router page:
/**
* Sample REST resource showing how to implement a "router" resource page.
*/
@Rest(
path="/",
title="Root resources",
description="Example of a router resource page.",
children={
HelloWorldResource.class,
PetStoreResource.class,
DtoExamples.class,
ConfigResource.class,
LogsResource.class,
ShutdownResource.class
}
)
public class RootResources extends BasicRestServletGroup {
// NO CODE!!!
}
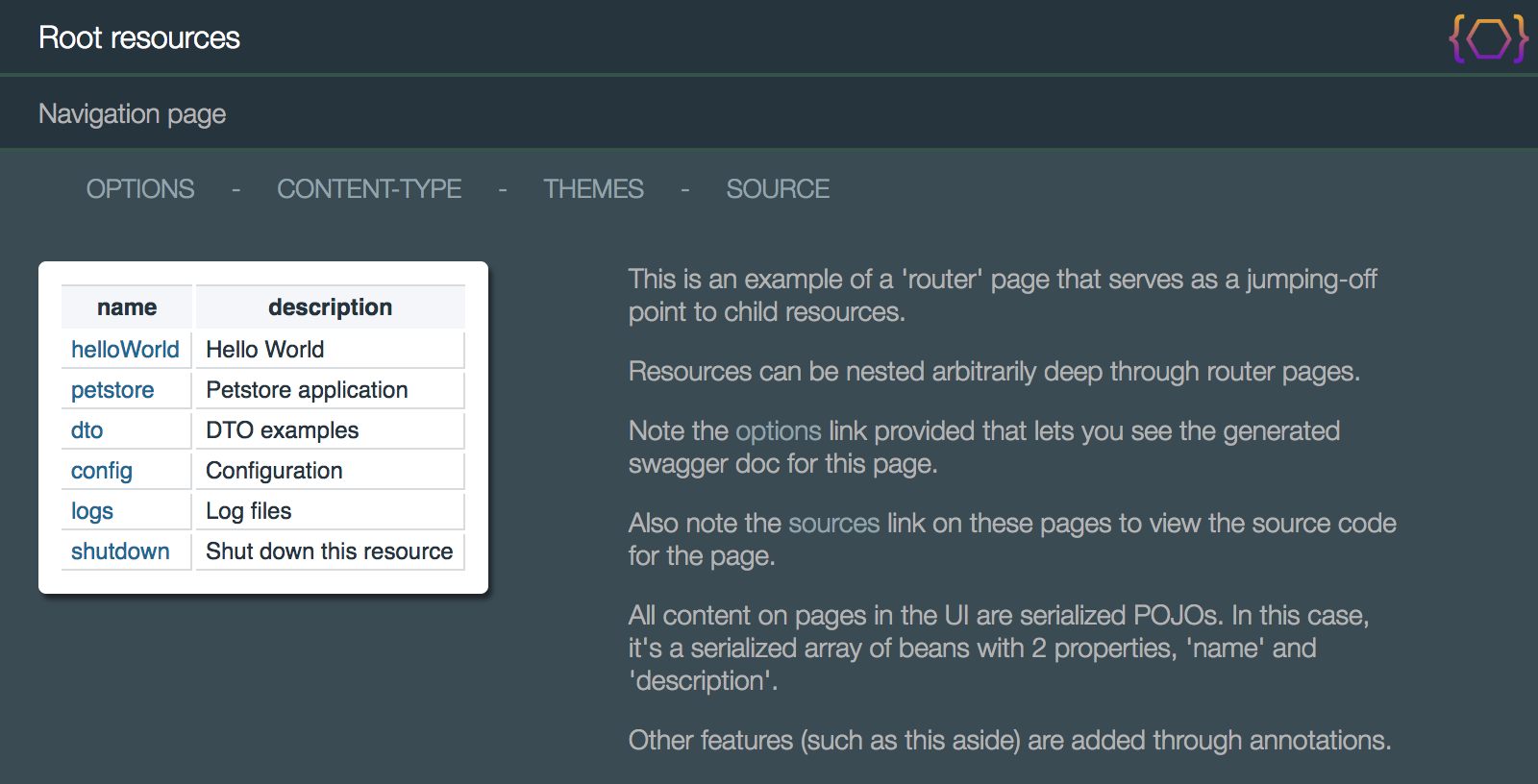
When you bring up this resource in a browser, you see the following that provides a list of navigable links to your child resources:
http://localhost:10000
REST Resource Methods
The real power behind the REST server API is the ability to define Java methods as REST endpoints.
@RestPost(path="/pets", guards=AdminGuard.class)
public Ok addPet(
@Content CreatePet createPetBean,
@Header("E-Tag") UUID etag,
@Query("debug") boolean debug
) throws BadRequest, Unauthorized, InternalServerError {
// Process request.
return Ok.OK;
}
Java methods on @Rest-annotated classes have the following format:
@RestOp(method="...", path="...")
public method() throws {
...
}
The various parts require their own topics to fully appreciate the scope of abilities but the following is a summary:
- Annotated with @RestOp.
- Also available: @RestGet / @RestPut / @RestPost / @RestDelete.
- Annotation optional if using standard naming conventions (e.g.
getFoo()equivalent to@RestGet(path="/foo")). - Optionally annotated with config annotations such as @BeanConfig and @HtmlDocConfig that customize the behavior of serializers and parsers at the method level.
- Returned object gets serialized as the HTTP response body.
- Typically a POJO serialized based on Accept request header.
- Support for raw values such as
ReadersandInputStreams(among others). - Support for response beans annotated with @Response.
- Support for Apache Http Core interfaces: HttpEntity / HttpResponse / HttpResource.
- Standard HTTP responses such as Ok and TemporaryRedirect provided in org.apache.juneau.http.response package.
- Extensible API for defining custom return types.
- A wide range of possible argument types including:
- Standard HttpServletRequest / HttpServletResponse objects.
- Extended RestRequest / RestResponse objects.
- Parsed HTTP parts with either the arguments or beans annotated with @Path / @Header / @Query / @FormData.
- Parsed HTTP body with either the argument or bean annotated with @Content.
- Raw HTTP request body with
InputStreamorReader. - Raw HTTP response body with
OutputStreamorWriter. - Request beans annotated with @Request.
- Response beans annotated with @Response.
- Standard HTTP headers such as Accept and ContentType provided in org.apache.juneau.http.header package.
- Auto-generated Swagger.
- Various other standard objects such as Principal, Cookie, HttpSession, and ResourceBundle.
- Spring beans or other injectable beans.
- Extensible API for defining custom argument types.
- Throwables can be anything.
- Typically one of the standard HTTP responses such as BadRequest or NotFound provided in org.apache.juneau.http.response package.
- Can define your own @Response-annotated throwables.
- Anything else gets converted to an InternalServerError.
Deploying as a Servlet
The BasicRestServlet class is the entry point for
your REST resources.
It extends directly from HttpServlet and is deployed like any other servlet (such as a standard web.xml file).
When the servlet init() method is called, it triggers the code to find and process the @Rest annotations on that class
and all child classes.
These get constructed into a RestContext object that holds all
the configuration information about your resource in a read-only object.
Most developers are not going to be using the RestServlet class itself, and instead will extend from one of the preconfigured default servlets such as BasicRestServlet and BasicRestServletGroup which provides universal language support, basic instrumentation, and auto-generated Swagger UI.
Deploying in Spring Boot
The BasicSpringRestServlet class is typically entry point for your REST resources when working within a Spring Boot environment. It extends from SpringRestServlet which provides additional capabilities including:
- Your REST resources can be defined as injectable Spring beans.
- Various capabilities within the REST Server library (e.g. logging, instrumentation, call handling, API extensions) can be defined via
Spring beans and automatically pulled into the framework.
Most developers are not going to be using the RestServlet class itself, and instead will extend from one of the preconfigured default servlets such as BasicSpringRestServlet and BasicSpringRestServletGroup that have the same capabilites as the BasicRestServlet and BasicRestServletGroup counterparts.
@Configuration
public class MySpringConfiguration {
/**
* Our root REST bean.
* Note that this must extend from SpringRestServlet so that child resources can be
* resolved as Spring beans.
* All REST objects are attached to this bean using the Rest.children() annotation.
*/
@Bean
public RootResources getRootResources() {
return new RootResources();
}
/**
* Optionally return the HelloWorldResource object as an injectable bean.
*/
@Bean
public HelloWorldResource getHelloWorldResource() {
return new HelloWorldResource();
}
/**
* Map our servlet to a path.
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getRootServlet(RootResources rootResources) {
return new ServletRegistrationBean(rootResources, "/*");
}
}
@Rest(
children={
HelloWorldResource.class
}
)
public class RootResources extends BasicSpringRestServletGroup {
// No code!
}
juneau-rest-server for more information.
Share feedback or follow-up questions for this page directly through GitHub.